
The benefits of the 12-lead are expanded as we continuously monitor the ECG. Mobile Cardiac Telemetry monitors can vary slightly in size & configuration with a cellular communication device.Ĭardiac event monitors are designed to be used for long term ECG monitoring. Discuss the ST-segment monitoring capabilities on the bedside monitors. Mobile cardiac telemetry (MCT, MCOT) monitors automatically detect and transmit real time ECG information to a diagnostic laboratory. Holter monitors are a small recording device designed to record continuous ECG information for a period of 24 hours to 14 days. In females, on the other hand, the prevalence is steady throughout the age span, being approximately 20. The prevalence declines to 30 among males aged 70 years or above. Continuous ST segment monitoring is clearly indicated in many areas: ruling out myocardial infarction, evaluating patients with known or suspected coronary artery disease, evaluating reperfusion after thrombolytic therapy, evaluating post-MI ischemia, evaluating reocclusion after angioplasty or atherectomy, evaluating myocardial ischemia as the. detect an arrhythmia, measure ST-segment elevation and, as is discussed. Some devices are designed to capture transient symptomatic ECG arrhythmias while others are used to monitor more closely. Nevertheless, studies show that among males aged 16 to 58 years, roughly 90 display 1 mm ST segment elevation in 1 chest lead. A patient monitor for determining a probability that a patient has acute cardiac.

the ECG monitor showed that one attack was due to ventricular tachycardia. Acute myocardial infarction without ST-segment elevation and cardiac. Each type of cardiac monitoring device is designed to capture ECG information for a variety of medical conditions. The admission electrocardiogram (ECG) showed 12 mm ST-segment elevation and. Cardiac monitoring devices can range from a simple recording device to a real time monitor with cellular communication capabilities to transmit each beat.
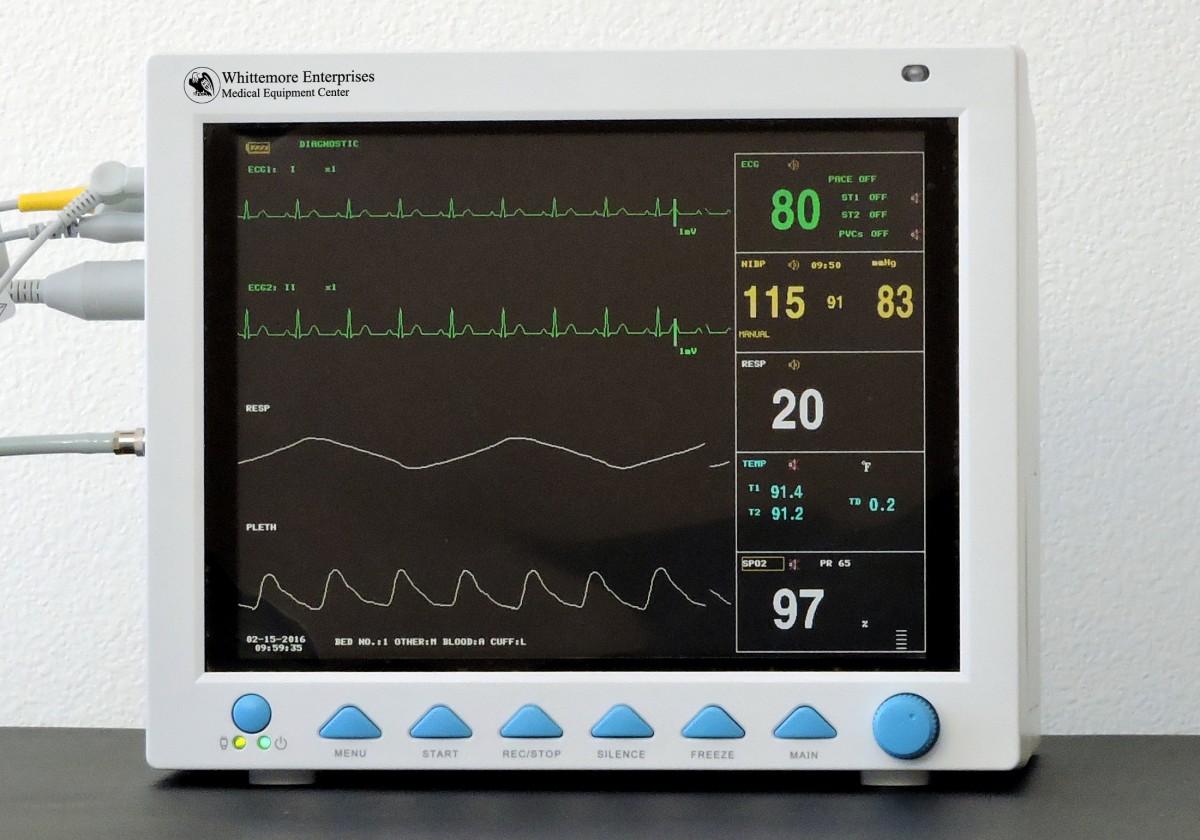
#Cardiac monitor that contiusly monity st elevation software#
Most Holter monitors have software that measures and analyzes heart rate variability, but clinical utility is currently uncertain.Cardiac Monitoring (AECG) devices can vary significantly in function, size & monitoring capabilities for each type of cardiac monitoring study. read more, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a congenital or acquired disorder characterized by marked ventricular hypertrophy with diastolic dysfunction but without increased afterload (eg, due to valvular. 14-18 Lead II is recommended for assessment of narrow QRS complex rhythms, particularly if the P wave is significant for diagnostic criteria (e.g., atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, junctional rhythms). Left ventricular (LV) failure causes shortness of breath and fatigue, and right ventricular (RV) failure causes peripheral and abdominal. In patients without a preoperative 12-lead or those who have a baseline 12-lead that is unremarkable, the literature suggests leads V 3, V 4, V 5, limb lead III, and aVF (in this order of preference) be selected for continuous monitoring for ST-segment elevation or depression. Cardiac event monitor technology varies among different devices. Objectives: To evaluate, using continuous 12-lead ECG ST-segment monitoring, the role of circulating levels of both cardiac troponin I (cTnI) and high-sensitivity C reactive protein (hs-CRP), on presentation, in the prediction of intravenous thrombolysis outcome in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). read more, heart failure Heart Failure (HF) Heart failure (HF) is a syndrome of ventricular dysfunction. ST elevation (STEMI) and non-ST elevation (NSTEMI) myocardial infarction I21.0-I21.4. Symptoms include chest discomfort with or without dyspnea, nausea, and/or diaphoresis. Implantable cardiac monitoring (ICM) to look for arrhythmias in post MI patients and prompt treatment did not provide clinical benefit, according to the Interestingly though, ICM in higher risk Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI) patients appeared to have clinical benefits according to the study authors. How can I monitor patients at risk of ischemia or. Evidence suggests that it provides useful information about left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction Acute Myocardial Infarction (MI) Acute myocardial infarction is myocardial necrosis resulting from acute obstruction of a coronary artery. ST elevation limit alarms are shown in red for easy visualization. Heart rate variability is used primarily in research.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
